Recent Articles Related To Physics
A metallic bar of Young’s modulus, 0.5 ×10^11 N m^–2 and coefficient of linear thermal expansion 10^–5 °C^–1, length 1 m and area of cross-section 10^–3 m^2 is heated from 0°C to 100°C without expansion or bending. The compressive force developed in it is
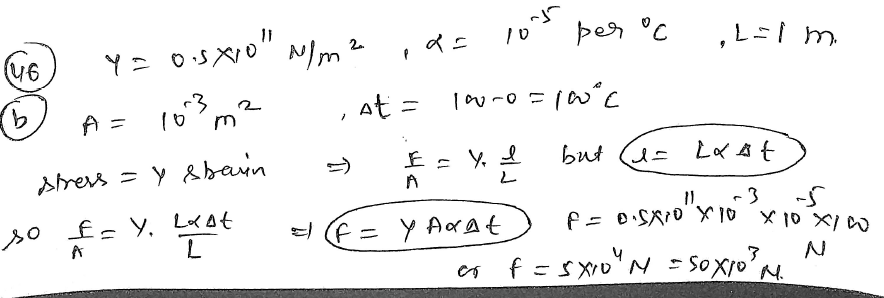
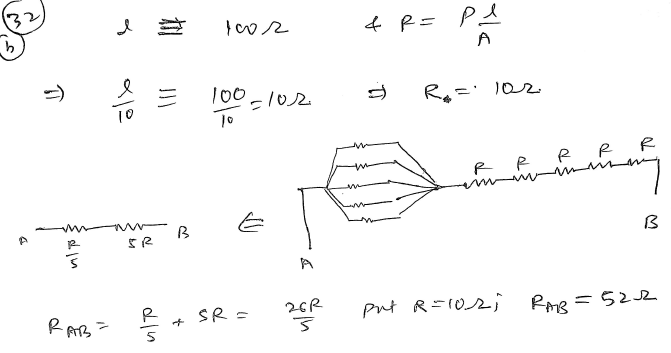
A wire of length ‘l’ and resistance 100 Ω is divided into 10 equal parts. The first 5 parts are connected in series while the next 5 parts are connected in parallel. The two combinations are again connected in series, Find final resistance.
Properties of an electromagnetic wave travelling in free space.
1.They travel with a speed equal to c.
2.they are transverse in nature.
3. They are originated from accelerated charges.
4.The energy density in electric field is equal to energy density in magnetic field.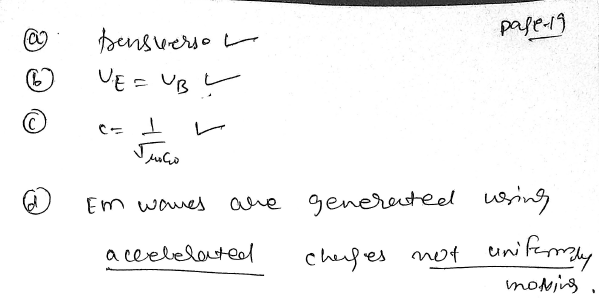
Acceleration and velocity of a particle moving with uniform speed in a circular path ? NEET UG2024
The acceleration of the particle in unifrom circular motion (constant speed) is constantly changing in direction as it is always directed towards the center. Hence , it is said to be variable.
As direction of velocity too is continuously changing so it is said to be variable velocity.
A thin spherical shell is charged by some source. The potential difference between the two points one is center C and other is at surface P (in V) will be ? NEET UG2024

A thin flat circular disc of radius 4.5 cm is placed gently over the surface of water. If surface tension of water is 0.07 Nm^–1, then the excess force required to take it away from the surface is? NEET UG2024

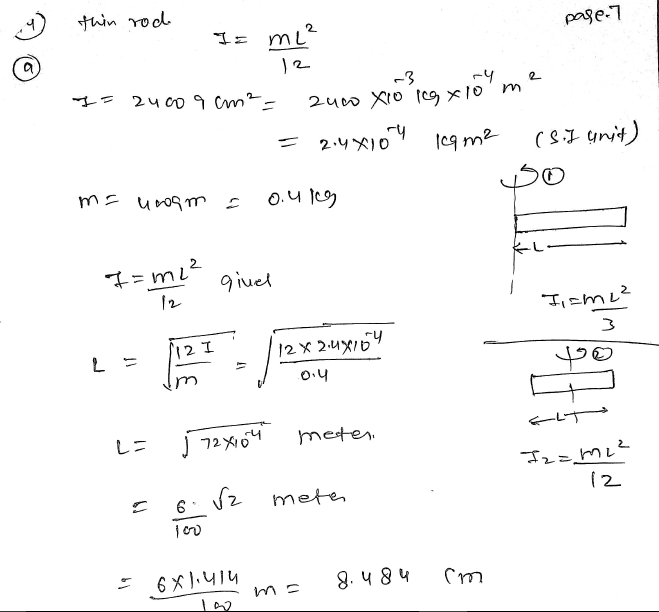
The moment of inertia of a thin rod about an axis passing through its mid point and perpendicular to the rod, is 2400 g cm^2. The length of the 400 g rod is nearly ?NEET UG2024
A bob is whirled in a horizontal plane by means of a string with an initial speed of ω rpm. The tension in the string is T. If speed becomes 2 ω while keeping the same radius, the tension in the string becomes? NEET UG2024
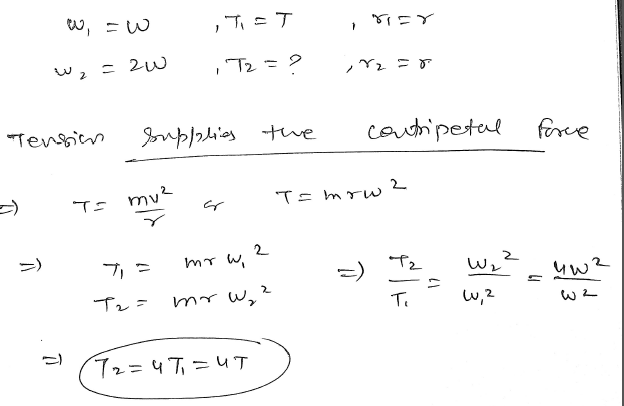
Calculating the minimum energy required to launch a satellite of mass m from the surface of earth of mass M and radius R in a circular orbit at an altitude of 2R from the surface of the earth. NEET UG2024
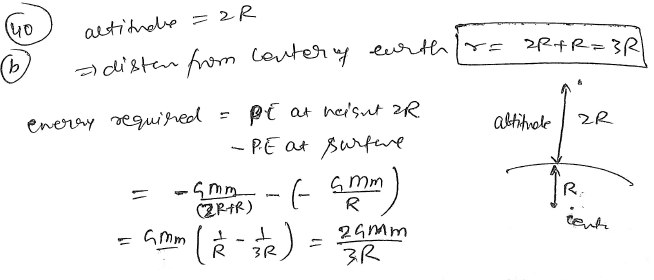
Short note about galvanometer, ammeter, voltmeter and shunt.
Galvanometer is a device used to detect and measure small currents and also direction of current, it measures current of the order of micro ampere. Due to its high sensitivity, high current may damage it.
Ammeter is used for measuring current and it is connected in series with the component for which we wish to know the current flowing through.
As the ammeter is connected in series (in series resistance is added directly) with the circuit so its resistance should be as minimum as possible so that it can't affect the net resistance leading to neligible effect on current already flowing in the circuit. Resistance of an ideal ammeter is zero.
Shunt is a low resistance connected in parallel with a device to reduce the amount of electric current flowing though it(device).
Note- " A galvanometer can be converted to an ammeter by connecting a shunt parallel to it."
Not in series because in that case it can increase net resistance.
Voltmeter is a device used to measure potential difference between two points in a circuit. It is connected in parallel with the device for which the potential difference betweeen its both ends is desired.
As voltmeter is connected in parallel so to ensure a very low or negligible current through it, its resistance is kept very high, for an ideal voltmeter its resistance is infinite.
"If current through voltmeter is considerable then it would mean that it hampered net current leading to incorrect measurement of potential difference(PD)."
Note- "A galvanometer can be converted to a voltmeter by connecting a high resistance in series with it."